
Book an Appointment
Call Us01140846835Epilepsy: Diagnosis and Treatment in Delhi
Epilepsy — also referred to as a seizure disorder — is a long-term brain disorder that results in recurrent, unprovoked seizures caused by abnormal brain electrical activity. Epilepsy has numerous forms, and although the cause of the epilepsy in some instances can be determined, in most instances it is unknown.
Did you know? Epilepsy is prevalent, impacting approximately 1.2% of Americans (as reported by the CDC) and millions globally, including in India. It occurs in individuals of all ages, races, and genders.
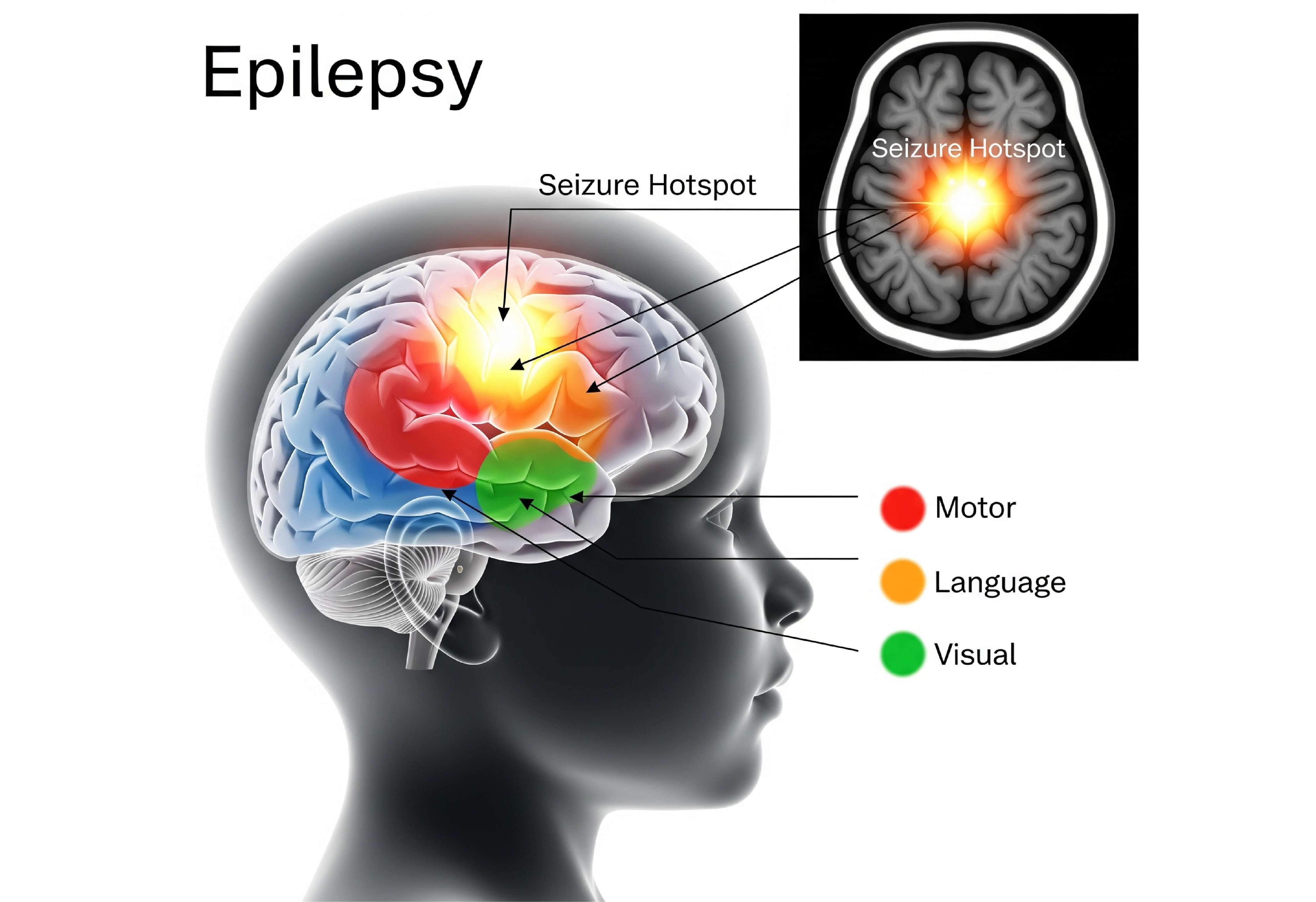 What Are Seizures?
What Are Seizures?
Seizures are caused by a sudden surge of electricity in the brain, which takes over the normal functioning of the brain for a temporary period of time. Seizures have different symptoms, depending on the region of the brain that is affected.
A few seizures result in short loss of awareness (e.g., blank staring), while others include involuntary jerking (convulsions).
Note: A single seizure doesn't necessarily mean you have epilepsy.
Epilepsy is diagnosed when you've had two or more unprovoked seizures at least 24 hours apart.
Read Also: Epilepsy Management in Delhi: Diet Therapy & Deep Brain Stimulation
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Symptoms vary with the type of seizure and what processes in the brain are affected. Common symptoms are:
- Brief confusion
- A spell of staring
- Stiffened muscles
- Uncontrollable jerking of the arms and legs
- Loss of consciousness
- Psychological symptoms such as fear, anxiety, or déjà vu
- Behavioral changes and psychotic symptoms can also occur in others.
Read Also: How Can Epilepsy Impact Your Lifestyle?
Warning Signs of Seizures (Aura)
Some individuals with focal seizures have a warning sign or aura just before a seizure occurs.
They may include:
- A strange sensation in the stomach or rising sensation
- Sudden fear or anxiety
- Déjà vu
- An unusual taste, smell, or visual event (e.g., flashing lights)
- Dizziness or hallucinations
Read Also: Can A Person Live a Normal Life with Epilepsy?
Types of Seizures
Seizures are divided into focal seizures (which start in one area of the brain) and generalized seizures (affecting the entire brain).
1. Focal Seizures
Without loss of consciousness (Simple partial):
Produce abnormal emotions, sensory phenomena, or jerking movement of a limb.
With impaired awareness (Complex partial):
Produce loss of awareness or responsiveness, staring spells, or repetition.
Examples of focal seizures:
- Temporal Lobe Seizures: Related to emotion, memory alteration, or automatic behaviors such as lip-smacking.
- Frontal Lobe Seizures: Produce unusual movements, laughter, or bicycle-pedaling movements.
- Occipital Lobe Seizures: Impact vision, leading to hallucinations or temporary loss of vision.
Read Also: Neurological Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
2. Generalized Seizures
- Absence seizures (Petit mal): Staring spells, a common pattern in children.
- Tonic seizures: Sudden stiffening of back, arms, and legs.
- Atonic seizures (Drop attacks): Sudden loss of muscle tone leading to falls.
- Clonic seizures: Rhythmic jerking of face, arms, or legs.
- Myoclonic seizures: Sudden brief jerks of upper body or limbs.
- Tonic-clonic seizures (Grand mal): Stiffening of the body, twitching and shaking, loss of consciousness, and bladder loss at times.
Read Also: All you need to know about Deep Brain Stimulation
When to See a Doctor
Contact a doctor immediately if:
- A seizure continues for over 5 minutes.
- Resolves neither breathing nor consciousness after the seizure.
- Suddenly another seizure follows.
- You are pregnant, diabetic, or hurt while seizing.
- Experience a first-time seizure.
Causes of Epilepsy
In approximately 50% of instances, there is no known cause of epilepsy. In the remaining instances, potential causes are:
- Genetic: Certain forms run in families or are associated with certain genes.
- Head trauma: Trauma from accidents.
- Abnormalities of the brain: Tumors, malformations of blood vessels, or scarring.
- Stroke: A major cause in people aged more than 35 years.
- Infections: Viral encephalitis, meningitis, HIV, or parasitic infections.
- Birth injury: Deprivation of oxygen or maternal infection during pregnancy.
- Developmental conditions: Autism, ADHD, and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
Seizure Triggers
Triggers don't cause epilepsy but can bring on seizures:
- Alcohol or drug use
- Flashing lights
- Missing anti-seizure medications
- Lack of sleep
- Stress or hormonal fluctuations (e.g., during menstrual cycles)
- Dehydration or missed meals
Risk Factors
You might have a greater chance of having epilepsy if you:
- Are a child or older adult (age-related risk peaks)
- Have a family history of epilepsy
- Have had a head injury
- Have vascular disease or a stroke
- Had dementia or brain infections (e.g., meningitis)
- Had seizures caused by fevers in childhood
Epilepsy Complications
- Injury: Seizures may lead to falls or accidents that result in fractures or head trauma.
- Risk of drowning: 13–19 times greater than the general population because seizures occur in water.
- Car accidents: Because of seizure-related loss of control.
- Pregnancy complications: Anti-seizure medicines can be harmful to the baby.
- Memory loss: Recurring seizures cause chronic cognitive effects.
- Mental illness: Depression, anxiety, or suicidal ideation.
Life-threatening complications:
- Status Epilepticus: Continuous seizures lasting >5 minutes or back-to-back seizures without regaining consciousness.
- Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP): A rare but serious risk, especially in people with uncontrolled tonic-clonic seizures.
Diagnosis of Epilepsy in Delhi
IBS Hospital, Delhi’s top hospital, provide state-of-the-art diagnostics, including:
- Neurological exam (behavior, motor skills, reflexes)
- Blood & genetic testing
- EEG & High-density EEG
- CT & MRI scans (including fMRI)
- PET & SPECT (SISCOM mapping)
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- Neuropsychological assessments
Treatment Plans for Epilepsy in Delhi
The majority of patients with epilepsy control medications, while some need surgery or newer treatments.
1. Medications (Anti-seizure medicines)
- Initial treatment in 50–60% of patients.
- Neurologists in Delhi tailor treatment according to the seizure type, age, and medical history.
2. Surgery for Epilepsy
In case of treatment failure (drug-resistant epilepsy), surgery can be indicated:
- Temporal Lobectomy
- Lesionectomy
- Corpus Callosotomy
- MRI-Guided Laser Ablation
Success Rate in India:
- 70–80% seizure-free results in temporal lobe epilepsy.
3. Advanced Therapies in Delhi
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): Decreases frequency of seizures by 20–40%.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Medanta, AIIMS.
- Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): Soon available in India.
4. Ketogenic & Modified Atkins Diet
- Effective in children and adults with resistant epilepsy.
- Dietitian-based ketogenic programs are available in Delhi hospitals such as Sir Ganga Ram and Apollo.
5. Emerging Treatments in Delhi
- MRI-guided focused ultrasound (non-surgical option)
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
Why Choose Delhi for Epilepsy Care?
- Expert epileptologists & neurosurgeons
- Advanced imaging and diagnostic tools
- Affordable treatment compared to global costs
- Comprehensive rehabilitation and counseling services
Conclusion
Epilepsy is a manageable condition with the right diagnosis and treatment. Delhi’s neurology centers combine modern technology, experienced specialists, and holistic care to help patients lead a seizure-free life.
 By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
July 30, 2025 | 9 Min Read
By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
July 30, 2025 | 9 Min Read
Best Tips for Sports Injury Recovery
Guide to Stroke Prevention and Recovery
How to Manage Parkinson’s Symptoms Effectively
Traumatic Brain Injury: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
10 Superfoods That Boost Your Brain Power
10 Early Warning Signs of Brain Stroke Everyone Should Know
5 Most Common Sports Injuries and Their Quick Treatments
12 Everyday Habits That Damage Your Spine
Brain Stroke: Causes, Warning Signs & Emergency Treatment
10 Early Symptoms of Brain Tumor You Should Never Ignore
How to Choose the Right Neurosurgeon in Delhi NCR
How Stress Affects Brain Health: Neurological Insights
Early Signs of Spinal Disorders in Working Professionals
How Advanced Neurosurgery Is Saving Lives: A Look Inside IBS Hospitals
Stroke Recovery: How a Comprehensive Neuro Rehab Plan Makes the Difference
Early Signs of Brain Tumor You Should Never Ignore
Benefits of Neuro-Navigation in Brain Surgery
Warning Signs Of Stroke You Should Never Ignore
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorders Early: Why It Matters
Spine Surgery vs Physiotherapy: Which Is Better for Back Pain?

