Book an Appointment
Call Us09958011121Hemorrhagic Stroke: What You Need to Know
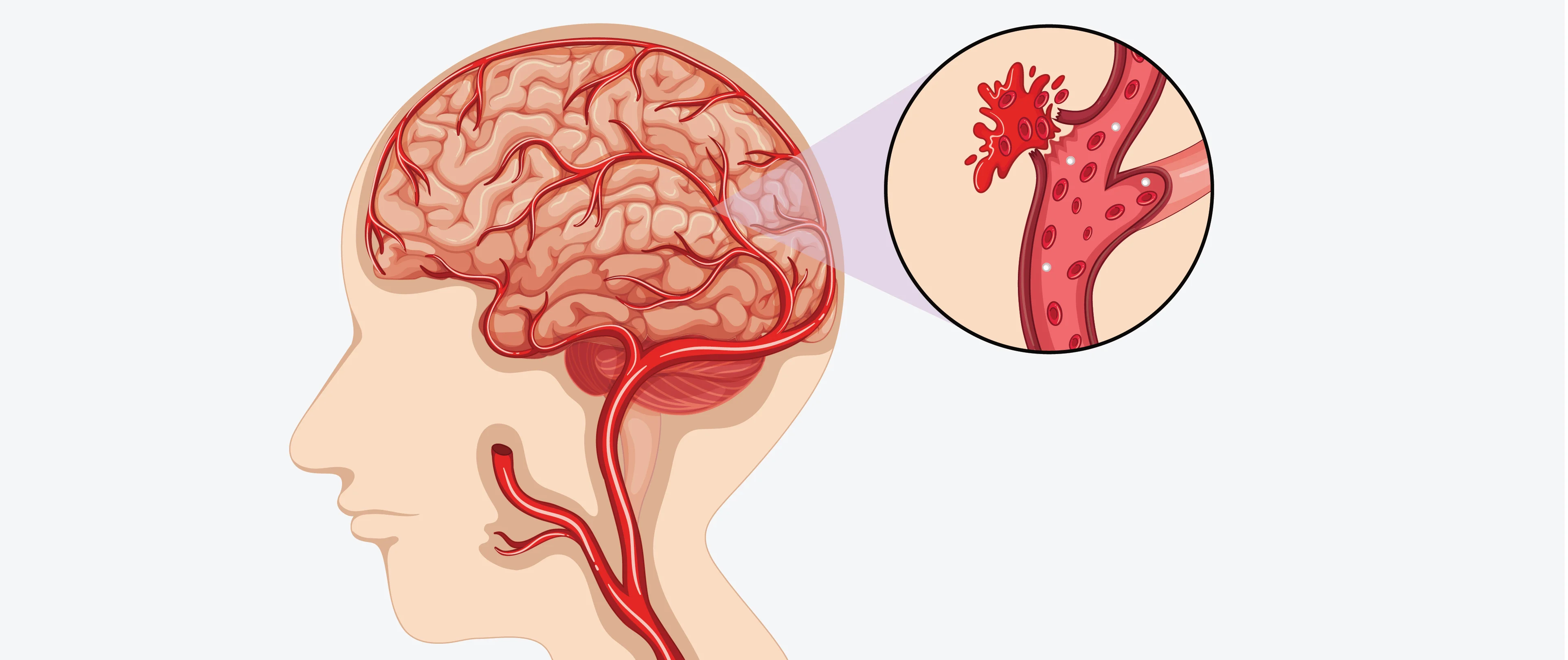
A hemorrhagic stroke is a severe, life-threatening condition involving uncontrolled bleeding within the brain or between it and its outer covering layer. It disrupts blood circulation, causing oxygen deprivation and pressure on surrounding brain areas. Without prompt medical attention, these strokes can lead to permanent brain damage or even death. It is crucial to call the emergency number immediately if symptoms arise. Best stroke treatment in Delhi is provided at IBS Hospital with their ultra modern treatment modalities and round the clock emergency services.
Warning Signs Of Stroke
To recognize the warning signs of a stroke, remember to think FAST:
- F for face: Ask the person to smile. Look for a droop on one or both sides of the face, which indicates muscle weakness or paralysis.
- A for arm: A person suffering from a stroke frequently experiences muscle weakness on one side. Ask them to lift their arms. If they develop one-sided weakness (which they did not have before), one arm will remain elevated while the other will sag and drop below.
- S for speech: Strokes frequently cause people to lose their ability to talk. They may slur their speech or have difficulty selecting the correct words.
- T for time: Avoid delaying getting help because time is crucial. If possible, look at your watch or a clock to remember when the symptoms start. Telling a healthcare provider when your symptoms begin will help them determine which treatment options will work for you.
Hemorrhagic strokes are most common in individuals with circulatory system diseases, especially the heart and blood vessels, and are more prevalent as people age.Approximately two-thirds of all strokes occur in persons over the age of 65. However, they can also occur in persons who have more serious health difficulties earlier in life.
Types Of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke can occur in any of two ways:
Internal bleeding in the brain: This produces bleeding inside your brain, which puts pressure on the surrounding brain tissue from within.
Bleeding into the subarachnoid area:Your brain is surrounded by the arachnoid membrane, a thin layer of tissue named for the spider web-like appearance on its surface. The subarachnoid space is the space between that membrane and your brain. If any blood vessels passing through the arachnoid membrane rupture, bleeding from them can flood the subarachnoid space. This creates pressure inside your skull from outside the brain itself.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke may include any of the following:
- Headaches (specialists commonly refer to these as "thunderclap" headaches since they are sudden and violent, similar to an unexpected thunderclap).
- Light sensitivity occurs when bright lights induce significant headache-like suffering (photophobia)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Passing out or fainting
- Coma
- Aphasia is characterized by difficulty or loss of speaking ability, as well as slurred or confused speech
- One-sided weakness, paralysis, or lack of tactile sensitivity
- One-sided loss of all two-sided senses (vision, hearing, and touch)
- Neck stiffness
Causes
The most common cause of hemorrhagic stroke is elevated blood pressure (hypertension). This is especially true when a person's blood pressure is extremely high, remains high for an extended time, or both. Other conditions or causes of hemorrhagic strokes are:
- Brain aneurysms
- Brain tumor
- Conditions that involve weakened blood vessels in your brain(moyamoya disease or cerebral amyloid angiopathy)
- Blood-thinners
- Head injuries
- Ischemic stroke that had secondary bleeding.
Other conditions and circumstances that may contribute to high blood pressure or your overall risk of having a stroke include:
- Alcohol use disorder.
- High blood pressure
- Hyperlipidemia
- Migraine headaches
- Smoking and other forms of tobacco use
Type 2 diabetes
Diagnosis and Tests
A healthcare provider will perform a neurological examination, diagnostic imaging, and other testing to diagnose a hemorrhagic stroke. Because many people who have a hemorrhagic stroke are unconscious, they are sometimes unable to answer questions or follow instructions from the doctor during a neurological examination. As a result, providers will frequently test certain reflexes and search for changes in processes that you cannot control, such as how your pupils react to light. Even if you are not awake, these can provide important clues for doctors to diagnose a hemorrhagic stroke.When a healthcare provider detects a hemorrhagic stroke, the following tests are typically performed:
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan.
- Lab blood tests
- Electrocardiogram
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Food Alteration
If you experience a hemorrhagic stroke (or any other type of stroke), your doctor may suggest that you change your diet to lower your blood pressure. Examples of this are:
Caffeine-containing beverages include coffee, tea, and soft drinks.
Salty or sodium-rich foods can raise blood pressure.
Meals high in saturated fat, such as fried dishes.
Alcohol or other drugs
Treatment
Hemorrhagic strokes are challenging to treat due to their difficulty in reaching directly. Priority is usually to reduce bleeding or stop it by boosting clotting processes and lowering blood pressure. Surgery may be necessary in some cases. Treatments depend on the stroke's location, severity, and other factors. Medications and treatments help regulate blood pressure and clot more effectively.Best stroke treatment and rehabilitation services are provided by IBS Hospital in Delhi.
Blood pressure management
Because high blood pressure is the most common cause of hemorrhagic strokes, decreasing and maintaining safe blood pressure is essential in treating these strokes. This can help minimize the amount of bleeding in your brain. It also promotes blood clotting and seals the damaged blood vessel.
Clotting support
Hemostasis, the process of forming a clot to repair an injury, is crucial in hemorrhagic strokes. To improve the effectiveness of hemostasis, medications or blood factors like vitamin K therapy and prothrombin or clotting factor infusions are often used.
Surgery
Hemorrhagic strokes can cause dangerous complications due to excessive blood pressure on brain tissue, necessitating emergency surgery to remove accumulated blood and relieve pressure buildup.
Stroke rehabilitation
Stroke patients often experience lingering effects, which can worsen in the first few days and improve over time. Different types of therapy and rehabilitation are beneficial for recovery, utilizing neuroplasticity in the brain. These methods help the brain re-map abilities, transferring control to undamaged parts, and speed up the recovery process.
Stroke rehabilitation can take many forms, including:
Speech therapy:This type of therapy focuses on the areas of your brain that control the ability to speak and understand what others are saying. It can also help if you have weakness or loss of control over the muscles of your mouth and throat. Speech therapy can help you not only speak, but also breathe, swallow, and eat or drink.
Physical therapy: This treatment method focuses on improving muscle strength and control, particularly in the arms, hands, legs, and feet. This type of treatment can help you relearn skills such as walking, clothing yourself, and eating. It can also help you adapt if you lose an ability permanently or for an extended period.
Cognitive therapy:This type of therapy improves your mental abilities. The primary goal of this type of therapy is to improve your cognitive, concentration, and memory capacities.
Other therapies are possible, based on your specific condition and circumstances. Your healthcare practitioner is the best person to inform you what therapies will help you.
Complications/side effects of the treatment
Stroke treatments can have varying side effects, depending on factors like cause, location, and medical history. Healthcare providers can provide information on these effects and prevent them. Stroke is a life-threatening emergency, so self-diagnosis is not recommended. Delaying diagnosis increases the risk of death or permanent brain damage. Factors influence recovery time, and healthcare providers are best equipped to provide guidance.
Prevention
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is crucial to prevent a hemorrhagic stroke. Manage health conditions like high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol. Maintain a balanced diet and healthy weight to prevent or delay stroke. Seek regular checkups with your primary care provider to detect potential stroke-causing issues early. Avoid risky lifestyle choices like smoking, drug misuse, and alcohol misuse. These changes can help prevent or reduce stroke severity. Regular checkups with your primary care provider can also help detect potential stroke-causing problems early.
Prognosis
A hemorrhagic stroke, characterized by sudden, severe symptoms, requires immediate medical attention. The stroke's location, bleeding severity, and prompt care significantly impact survival and recovery chances. Healthcare providers should discuss specific cases and circumstances to provide personalized guidance.
Hemorrhagic strokes have a less favorable outlook due to difficulty in stopping bleeding and requiring a small amount of blood to cause severe symptoms. Severe cases can lead to permanent coma, vegetative state, or locked-in syndrome. With fast medical care, some people can recover, but the outcome varies.
Conclusion
Hemorrhagic stroke patients should follow their healthcare provider's treatment recommendations, recovery timeline, and self-care. It is important to manage chronic health conditions, especially blood pressure, and attend follow-up care, therapy, and rehabilitation appointments. Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, can complicate recovery. Modifying lifestyles, such as diet, exercise, and quitting smoking, can help avoid future problems. Regular follow-up care with the healthcare provider is essential, including noticing new symptoms or changes in daily routines, even if they don't seem to be related to the stroke.
FAQs
Are hemorrhagic strokes contagious?
Hemorrhagic strokes aren’t contagious, and you can’t pass them from person to person.
How does this condition affect my body?
A hemorrhagic stroke results in severe bleeding in or around the brain, putting too much pressure on surrounding brain tissue, causing permanent damage. It also disrupts blood flow in the brain, similar to a hole in a straw, reducing blood flow to nearby areas.
Are hemorrhagic strokes contagious?
Hemorrhagic strokes are not contagious, and they cannot be passed from person to person.
 By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
March 21, 2024 | 9 Min Read
By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
March 21, 2024 | 9 Min Read
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Hospital in India
Brain Stroke Treatment Hospital – Emergency Care
Stroke Paralysis Treatment Hospital – Advanced Neuro Care
Paralysis Treatment Hospital in India – Cost & Recovery
Brain Infection Symptoms, Causes, and When to Seek Emergency Care
Is Spine Surgery Right for You? Here’s How to Know
Brain Health at Every Age: Preventive Neurology Tips
International Patient Guide: Visiting India for Neuro & Spine Treatments
Robot-Assisted & Navigation-Guided Surgery: Safer Brain & Spine Procedures
Sports Injury Recovery: How Arthroscopy Helps You Heal Faster?
How Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Helps in Parkinson’s & Tremor Control
Early Warning Signs of a Brain Tumour & When to See a Neurosurgeon
Signs of a Stroke: When to Seek Emergency Neuro Care
Best Neurosurgery Hospitals in Delhi NCR: A Detailed Guide
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Benefits, Cost & Recovery
Best Tips for Sports Injury Recovery
Guide to Stroke Prevention and Recovery
How to Manage Parkinson’s Symptoms Effectively

