Book an Appointment
Call Us09958011121Understanding Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke treatment is the most common form of stroke is ischemic, which occurs when arteries around the brain become blocked. These strokes can occur in a variety of locations across the body and may be caused by various types of blockages. A stroke happens when the body stops providing blood to the brain. Approximately 87% of all strokes are ischemic in nature. The next section discusses the causes of ischemic stroke, how to recognize it, and how to prevent and treat it.
What Are The Causes For Ischemic Stroke ?
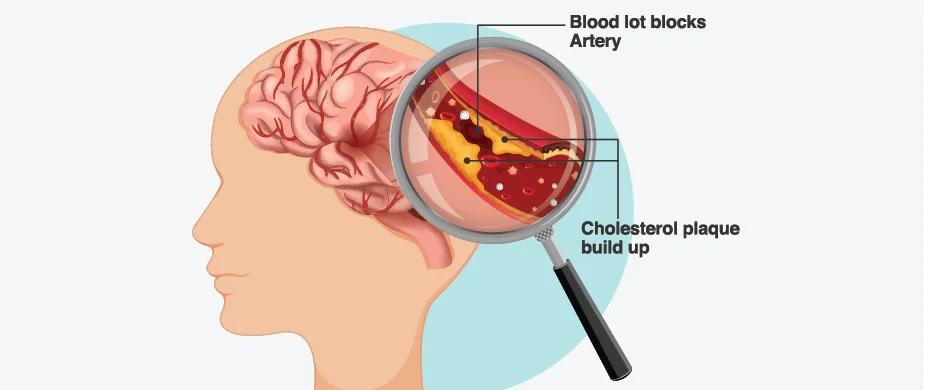
Ischemic stroke is the most common form, and early treatment is crucial. An ischemic stroke is caused by atherosclerosis, which causes fatty deposits and the deposition of cholesterol plaque in the blood vessels. When too much plaque accumulates in one area, it can obstruct blood flow to vital organs. A blood clot can stick to a deposit of plaque while flowing through the blood vessels, resulting in a blockage. The neck contains carotid arteries, which are blood channels that transport blood to the brain. A stroke can develop when plaque plugs into a carotid artery (carotid artery disease).
Atherosclerosis is usually symptomless. As a result, many people are unaware they have atherosclerosis until they have a stroke or suffer the severe consequences of blocked arteries near other organs, such as a heart attack.
Risk Factors Of Ischemic Stroke
The major risk factors for ischemic stroke and carotid artery disease are similar.
They include:
- High blood pressure:( leading cause of stroke)
- Diabetes:It increases the risk of carotid artery disease fourfold.
- Atherosclerosis or carotid artery disease: Having either of these conditions or a family history of them, can increase your chance of having a stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib): Approximately 15% of strokes occur in persons with Afib.
- Cholesterol levels: High levels of "bad" low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, as well as low levels of "good" high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, can contribute to the formation of plaque in arteries.
- Sedentary lifestyle: A lack of physical activity may lead to high blood pressure, cholesterol, and obesity. These raise the likelihood of arterial plaque accumulation.
- Being overweight or obese.
- An unhealthy diet: Consuming too much saturated or trans fats, as well as foods rich in cholesterol, sodium, and sugar, can result in diabetes, plaque accumulation, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol.
- Being more than 55 years old: People over the age of 55 are more likely to have a stroke, and this risk increases with each decade of life.
- People who have already experienced a transient ischemic attack (TIA) are also at risk for ischemic stroke. A transient ischemic attack, sometimes known as a "mini-stroke," is a momentary halt of blood flow to the brain.
A TIA has the same symptoms as an ischemic stroke, but it usually lasts less than 5 minutes and causes no permanent damage. Within a year, around one-third of all TIA patients will have a more severe stroke.
Another risk factor for ischemic stroke is smoking, which causes:
- Plaque formation in blood vessels
- Increases the risk of clotting,
- Raises cholesterol levels,
- Narrows blood vessels
- Damages the lining of blood vessels
All of these factors increase the chance of a stroke.
Types Of Ischemic Stroke
All ischemic strokes are caused by a cessation of blood supply to the brain. Ischemic strokes, contrary to belief, can begin in numerous parts of the body and can be caused by many different types of blockages.
Embolic stroke: It occurs when a blood clot, plaque, or another material forms in a different region of the body and travels to the brain's blood vessels.
Thrombotic stroke: It occurs when a clot or thrombus forms within a blood vessel in the brain.
Symptoms Of Ischemic Stroke
Strokes can be life-threatening, so seek medical attention as soon as symptoms develop.
Ischemic stroke symptoms typically affect one side of the body and appear quickly.
The American Stroke Association (ASA) suggests that people know F.A.S.T. This stands for:
F = Face drooping: People may notice that one side of their face droops or feels numb. Another person can check for this symptom by asking the individual to grin or stick out their tongue.If their smile has an asymmetry or their tongue goes to one side of the mouth rather than the center, it could be an indicator of an ischemic stroke.
A = Arm weakness: Being unable to lift one arm or experiencing weakness or numbness in one arm may indicate an ischemic stroke is occuring.
S = Speech issues: which can include being unable to speak or repeat a sentence.
T = Time to Call emergency services immediately and noting any other signs of an ischemic stroke.
Aside from F.A.S.T., a stroke may cause the following symptoms that appear suddenly:
Symptoms may include
- Difficulty in walking
- Disorientation
- Inexplicable falls
- Problems with comprehending speech
- Confusion
- Rapid vision impairment.
- An intense headache with no clear cause.
Treatment Of Ischemic Stroke
An emergency medical team will provide clot-busting drugs. IBS Hospital provides round the clock emergency ischemic stroke treatment in delhi. The brain requires a steady supply of oxygen-rich blood, so even a brief stoppage can cause brain cell damage and destruction.
With a stroke, every minute counts, and immediate treatment is critical for survival. A person suffering an ischemic stroke requires emergency treatment, which may include the following:
Medication: A member of the emergency team will administer tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), a clot-busting drug, via a vein in the arm.To have the intended effect, doctors must provide this drug within 4 hours of the onset of stroke symptoms.The chances of a positive outcome increase the sooner a person receives a tPA shot.
Surgery to remove clot: A mechanical thrombectomy may be performed after an ischemic stroke patient has received a tPA injection.
This surgery includes using a catheter to remove the clot, and doctors must perform it within 6 hours of the onset of symptoms.
Prevention Of Stroke
Anyone with risk factors or a history of stroke can take measures to improve their cardiovascular health and reduce their risk of having an ischemic stroke.The following steps can help avoid strokes and enhance general health:
Having Regular Checkups: High blood pressure and cholesterol have no apparent symbols. Regular health testing is the only way to determine whether these are present. Blood tests and health screenings can help discover these issues early and provide timely treatment.
Getting Regular Exercise: An active lifestyle lowers the risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and other disorders that raise the risk of an ischemic stroke.
A heart-healthy diet: It should be low in "bad" fats including saturated and trans fats. Individuals should also decrease their salt intake. Consuming more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins can help individuals maintain good cardiovascular health.
Managing body weight: If a person is overweight or obese, achieving a healthy body weight can reduce their stroke risk.
Avoiding firsthand or secondary smoking: Smoking and inhaling secondhand smoke can damage blood vessels and raise the risk of stroke-related health problems.
Being aware of your family history: Always share a family history of stroke or TIA with your doctor.
Taking daily aspirin: A doctor may advise a person who is at a particularly high risk of a heart attack or stroke but has a low risk of bleeding to take aspirin daily. Because of the increased risk of bleeding, guidelines no longer recommend that aspirin be used widely for this reason.
Getting enough sleep and controlling stress: Getting 7-8 hours of sleep and using stress-reduction strategies, such as meditation, may help to avoid strokes and improve your overall well-being.
Conclusion
A stroke can be frightening and can occur even in someone who appears to be in good condition. Knowing the warning signals and receiving immediate medical care are the most crucial steps toward improving a person's prognosis after a stroke.
If a friend or family member has a stroke, they should not be driven to the hospital. Instead, they should call an ambulance so that professionals may deliver medical assistance as soon as possible. An ambulance can also transport the patient to the hospital that can provide the greatest stroke care, which may not be the closest facility. A quick response significantly increases a person's chances of survival following a stroke.
The primary goal of therapy in acute ischemic stroke is to protect tissue in the ischemic penumbra, where perfusion is reduced but adequate to prevent infarction. Tissue in this area of oligemia can be saved by restoring blood flow to the affected area and enhancing collateral flow.
 By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
March 22, 2024 | 9 Min Read
By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
March 22, 2024 | 9 Min Read
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Hospital in India
Brain Stroke Treatment Hospital – Emergency Care
Stroke Paralysis Treatment Hospital – Advanced Neuro Care
Paralysis Treatment Hospital in India – Cost & Recovery
Brain Infection Symptoms, Causes, and When to Seek Emergency Care
Is Spine Surgery Right for You? Here’s How to Know
Brain Health at Every Age: Preventive Neurology Tips
International Patient Guide: Visiting India for Neuro & Spine Treatments
Robot-Assisted & Navigation-Guided Surgery: Safer Brain & Spine Procedures
Sports Injury Recovery: How Arthroscopy Helps You Heal Faster?
How Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Helps in Parkinson’s & Tremor Control
Early Warning Signs of a Brain Tumour & When to See a Neurosurgeon
Signs of a Stroke: When to Seek Emergency Neuro Care
Best Neurosurgery Hospitals in Delhi NCR: A Detailed Guide
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Benefits, Cost & Recovery
Best Tips for Sports Injury Recovery
Guide to Stroke Prevention and Recovery
How to Manage Parkinson’s Symptoms Effectively

