
Book an Appointment
Call Us09958011121Brain Stroke: Causes, Warning Signs & Emergency Treatment
What is a Brain Stroke
A brain stroke is a serious medical emergency of bleeding inside the brain. It occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked. It can be due to any reason, such as high blood pressure or plaque buildup.
Without an adequate oxygen and nutrient supply, brain cells begin to die within minutes. Early treatment is crucial to decreasing the damage and promoting smooth recovery. Being aware of the warning signs, especially BE FAST signs of stroke, can help save many lives and avoid long-term health complications.
Common Names of Brain Stroke
Some of the alternative names of a brain stroke are:
- Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
- Brain attack
- Mini-stroke (for a Transient Ischemic Attack, or TIA)
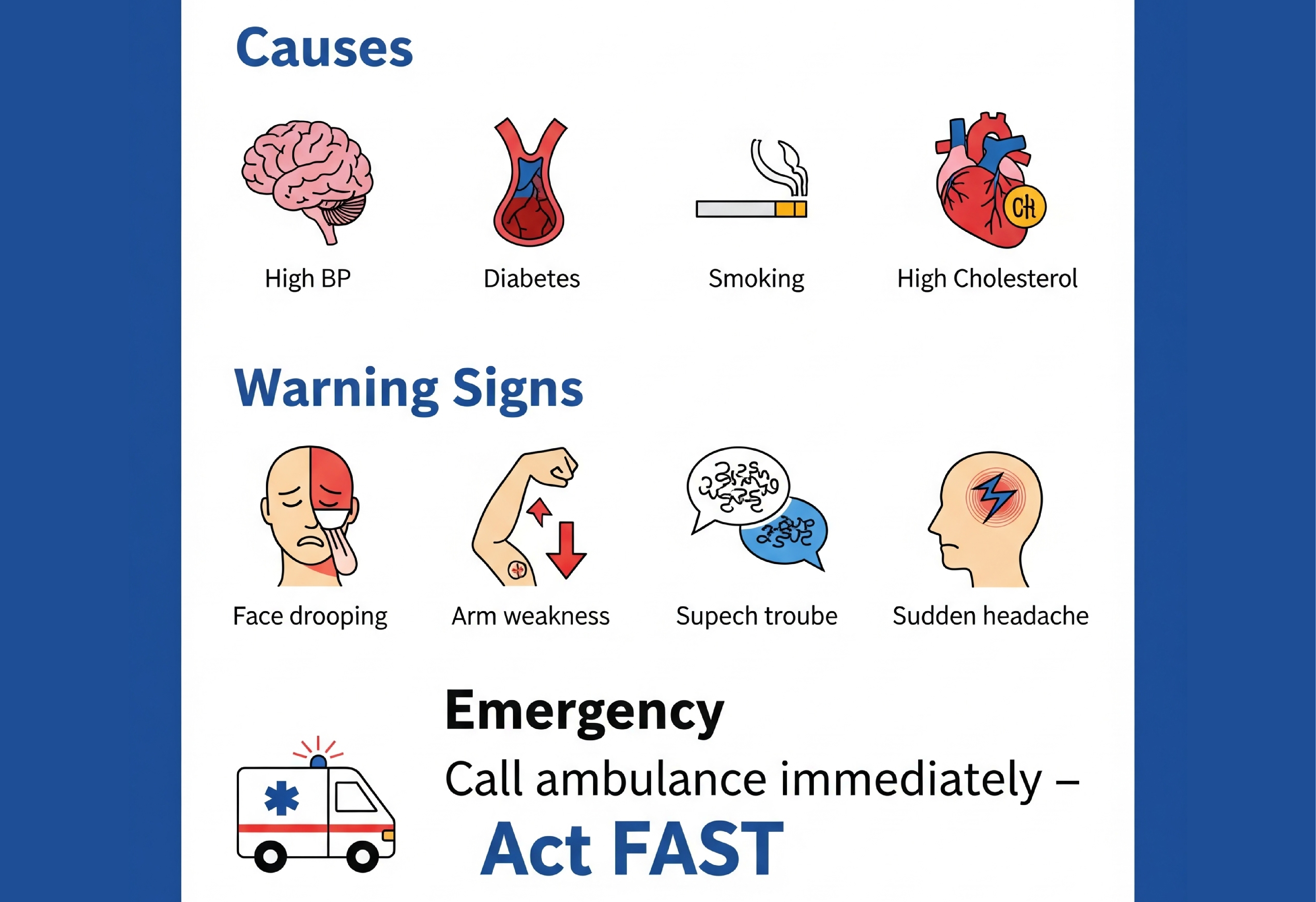
What are the Common Causes of Stroke
There are two types of brain stroke:
- Ischemic strokes: Blood clot blocks a blood vessel connected to the brain.
- Hemorrhagic strokes: Blood vessel in the brain breaks or tears.
Let's explore their causes individually.
Common Causes of Ischemic Strokes
- Atherosclerosis: Hardened or narrowed arteries lead to improper blood and clot formation.
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular heartbeat impairs the heart's pumping ability. This can let blood pool in the heart and cause clots.
- Clotting disorders: In some conditions, blood clots too easily, blocking the blood supply to the brain.
- Heart defects: Small birth defects in the heart may allow clots to enter the brain.
- Microvascular ischemic disease: Damage to tiny brain blood vessels decreases blood circulation, increasing stroke risk.
Common Causes of Hemorrhagic Strokes
- Brain aneurysms: There is a weak spot in the wall of the brain’s blood vessel, which could swell and burst, leading to a stroke.
- Brain tumors: Tumors can block blood vessels, decreasing blood flow to the brain.
- High blood pressure: Constant high blood pressure can damage vessels, causing them to clog or burst.
- Moyamoya disease: Narrow brain arteries force the brain to develop tiny, weak vessels that easily get clogged up.
Early Warning Signs of Stroke and Mini-Stroke
Some of the early warning signs of stroke and mini stroke are:
A. Early Warning Signs of Stroke
- One-sided weakness or numbness in your face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty in talking and walking
- Unexplained fainting and seizure
- Unable to understand what others are saying
- Unexplained, sudden, severe headache
- Blurred vision
- Double vision
- Loss of sight in one or both eyes
- Feeling dizzy or unsteady
- Struggling to keep your balance
Other less common signs are briefly losing consciousness, feeling confused, or slipping into a coma.
B. Early Warning Signs of Mini-Stroke
A transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or "mini stroke" occurs due to a brief disruption in the blood supply to part of the brain due to a lack of oxygen.
- One-sided weakness, numbness, or paralysis
- Slurred speech
- Balance and coordination issues
- Unable to understand others talks
- Loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Double vision
- Dizziness
Stroke risk factors
The following are the risk factors of stroke:
- People older than 65
- Smoke
- Use other forms of tobacco or nicotine (like vaping)
- Use recreational medicine
- Use of nonprescription drugs
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Type 2 diabetes
- Alcohol abuse
- COVID-19
- Frequent migraine headaches
What are the BE FAST Signs of Stroke
The acronym BE FAST stroke symptoms, stands for Balance, Eyes, Face, Arms, Speech, and Time. This helps you spot common stroke signs quickly:
Here is the expanded version:
- B - Balance: Difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of coordination.
- E - Eyes: Sudden blurred vision, double vision, or loss of sight in one or both eyes.
- F - Face: If smiling, one-sided facial drooping occurs.
- A - Arms: When lifting both arms, one drifts downward.
- S - Speech: Slurred speech or unable to comprehend others
- T - Time: If you notice any of these signs, call emergency services immediately, as every minute counts.
Emergency Treatment Guide for Brain Stroke
The emergency treatment guide is based on the following conditions:
- How much the stroke injured the brain
- Which region of your brain is affected
- Which type of stroke happened
7 Key Steps of Emergency Treatment Guide for Stroke
- Call for emergency help immediately
- Early paramedic treatment
- CT or MRI scans to help understand the type of stroke for the right treatment.
- For ischemic stroke, doctors may administer a clot‑busting medicine (tPA).
- For hemorrhagic stroke, doctors may use a surgical procedure, or endovascular repair may be needed to stop bleeding.
- Blood thinners, blood pressure medicines, and surgery, can be used to avoid repeat strokes.
- Speech, physical, and occupational therapy start early to regain movement and communication skills.
What to do During a Stroke
If you notice anyone having a stroke, you should do the following things:
- Call emergency services right away.
- Keep the person calm and comfortable.
- Help them sit or lie down in a safe environment.
- Loosen any tight clothing to ensure easy breathing.
- If the person is conscious, put them on their side with their head slightly raised. This will avoid choking.
- Do not give food, drink, or any medicine by yourself.
- Monitor their breathing.
- Be prepared to perform CPR if they cease breathing.
- Keep note of every symptom (time and intensity).
- Do not leave the person until help arrives.
How Can I Prevent a Stroke?
The ways to prevent a stroke are:
- Eat plenty of healthy foods
- Maintain a weight that’s healthy for you
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Manage your blood pressure, cholesterol
- Follow your doctor's prescription in case of any health condition
- Quit smoking
FAQs
Q: What is the stroke survival rate?
A: About 50-60% of people endure a stroke; however, survival depends on stroke type, age, and timely, appropriate treatment. Ischaemic strokes have a greater survival rate when compared to hemorrhagic ones.
Q: What is stroke recovery time?
A: Recovery varies across different individuals and depends on stroke severity and rehabilitation. Some may recover within weeks, while others may take months or even years.
Q: How do I take care of myself after a stroke?
A: Recovery from stroke becomes fast when you follow the points below:
- Take note of your doctor’s advice
- Take prescribed medication
- Take timely neurorehabilitation therapies
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Follow customized physical activity
- Control risk factors such as blood pressure and diabetes
Q: How do you feel after a stroke?
A: You can notice weakness, fatigue, challenges in movements or communicating, emotional changes, and cognitive impairment. Do not worry; they will improve over time following proper therapy.
Q: What to do if you have a stroke alone?
A: Call emergency services right away, try to be as calm as possible, lie down safely, and do not eat food or drink anything. Additionally, keep track of your symptoms until help arrives.
 By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
September 18, 2025 | 9 Min Read
By -Dr Aaksha Shukla |
September 18, 2025 | 9 Min Read
Parkinson’s Disease Treatment Hospital in India
Brain Stroke Treatment Hospital – Emergency Care
Stroke Paralysis Treatment Hospital – Advanced Neuro Care
Paralysis Treatment Hospital in India – Cost & Recovery
Brain Infection Symptoms, Causes, and When to Seek Emergency Care
Is Spine Surgery Right for You? Here’s How to Know
Brain Health at Every Age: Preventive Neurology Tips
International Patient Guide: Visiting India for Neuro & Spine Treatments
Robot-Assisted & Navigation-Guided Surgery: Safer Brain & Spine Procedures
Sports Injury Recovery: How Arthroscopy Helps You Heal Faster?
How Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Helps in Parkinson’s & Tremor Control
Early Warning Signs of a Brain Tumour & When to See a Neurosurgeon
Signs of a Stroke: When to Seek Emergency Neuro Care
Best Neurosurgery Hospitals in Delhi NCR: A Detailed Guide
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Benefits, Cost & Recovery
Best Tips for Sports Injury Recovery
Guide to Stroke Prevention and Recovery
How to Manage Parkinson’s Symptoms Effectively

